sfepy.homogenization.utils module¶
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.build_op_pi(var, ir, ic)[source]¶
Pi_i^{rs} = y_s delta_{ir} for r = ir, s = ic.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.create_pis(problem, var_name)[source]¶
Pi_i^{rs} = y_s delta_{ir}, ul{y} in Y coordinates.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.create_scalar_pis(problem, var_name)[source]¶
Pi^k = y_k, ul{y} in Y coordinates.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.define_box_regions(dim, lbn, rtf=None, eps=0.001, kind='facet')[source]¶
Define sides and corner regions for a box aligned with coordinate axes.
- Parameters:
- dimint
Space dimension
- lbntuple
Left bottom near point coordinates if rtf is not None. If rtf is None, lbn are the (positive) distances from the origin.
- rtftuple
Right top far point coordinates.
- epsfloat
A parameter, that should be smaller than the smallest mesh node distance.
- kindbool, optional
The region kind.
- Returns:
- regionsdict
The box regions.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.get_box_volume(dim, lbn, rtf=None)[source]¶
Volume of a box aligned with coordinate axes.
Parameters:
- dimint
Space dimension
- lbntuple
Left bottom near point coordinates if rtf is not None. If rtf is None, lbn are the (positive) distances from the origin.
- rtftuple
Right top far point coordinates.
Returns:
- volumefloat
The box volume.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.get_lattice_volume(axes)[source]¶
Volume of a periodic cell in a rectangular 3D (or 2D) lattice.
- Parameters:
- axesarray
The array with the periodic cell axes
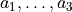 as rows.
as rows.
- Returns:
- volumefloat
The periodic cell volume
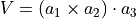 . In 2D
. In 2D
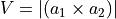 with zeros as the third components of
vectors
with zeros as the third components of
vectors 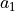 ,
, 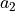 .
.
- sfepy.homogenization.utils.get_volume(problem, field_name, region_name, quad_order=1)[source]¶
Get volume of a given region using integration defined by a given field. Both the region and the field have to be defined in problem.