navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc.py¶
Description
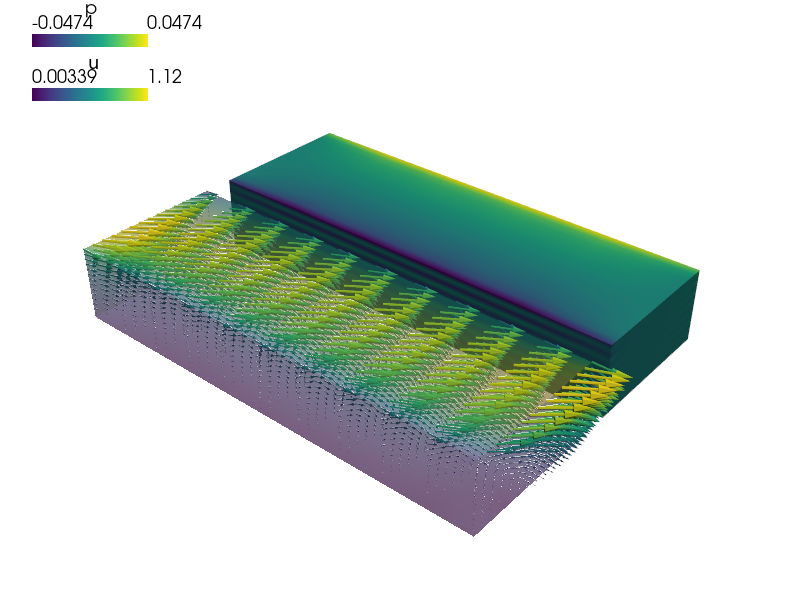
Incompressible Stokes flow with Navier (slip) boundary conditions, flow driven by a moving wall and a small diffusion for stabilization.
This example demonstrates the use of no-penetration and edge direction
boundary conditions together with Navier or slip boundary conditions.
Alternatively the no-penetration boundary conditions can be applied in a weak
sense using the penalty term dw_non_penetration_p.
Find 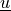 ,
, 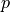 such that:
such that:
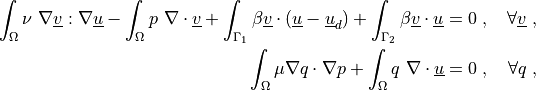
where 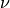 is the fluid viscosity,
is the fluid viscosity, 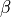 is the slip
coefficient,
is the slip
coefficient, 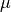 is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
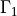 is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
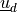 and
and 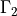 are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both
are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both 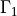 ,
, 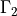 and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
The no-penetration boundary conditions are applied on 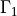 ,
,
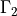 , except the vertices of the block edges, where the edge
direction boundary conditions are applied.
, except the vertices of the block edges, where the edge
direction boundary conditions are applied.
The penalty term formulation is given by the following equations.
Find 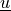 ,
, 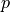 such that:
such that:
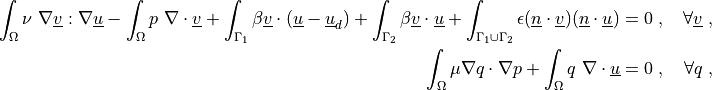
where  is the penalty coefficient (sufficiently large). The
no-penetration boundary conditions are applied on
is the penalty coefficient (sufficiently large). The
no-penetration boundary conditions are applied on 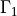 ,
,
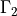 .
.
Optionally, Dirichlet boundary conditions can be applied on the inlet in the both cases, see below.
For large meshes use the 'ls_i' linear solver - PETSc + petsc4py are needed
in that case.
Several parameters can be set using the --define option of sfepy-run,
see define() and the examples below.
Examples¶
Specify the inlet velocity and a finer mesh:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d shape="(11,31,31),u_inlet=0.5"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Use the penalty term formulation and einsum-based terms with the default (numpy) backend:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Change backend to opt_einsum (needs to be installed) and use the quadratic velocity approximation order:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "u_order=2,mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum,backend=opt_einsum,optimize=auto"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Note the pressure field distribution improvement w.r.t. the previous examples. IfPETSc + petsc4py are installed, try using the iterative solver to speed up the solution:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "u_order=2,ls=ls_i,mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum,backend=opt_einsum,optimize=auto"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
r"""
Incompressible Stokes flow with Navier (slip) boundary conditions, flow driven
by a moving wall and a small diffusion for stabilization.
This example demonstrates the use of `no-penetration` and `edge direction`
boundary conditions together with Navier or slip boundary conditions.
Alternatively the `no-penetration` boundary conditions can be applied in a weak
sense using the penalty term ``dw_non_penetration_p``.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \nu\ \nabla \ul{v} : \nabla \ul{u}
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v}
+ \int_{\Gamma_1} \beta \ul{v} \cdot (\ul{u} - \ul{u}_d)
+ \int_{\Gamma_2} \beta \ul{v} \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\int_{\Omega} \mu \nabla q \cdot \nabla p
+ \int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;,
where :math:`\nu` is the fluid viscosity, :math:`\beta` is the slip
coefficient, :math:`\mu` is the (small) numerical diffusion coefficient,
:math:`\Gamma_1` is the top wall that moves with the given driving velocity
:math:`\ul{u}_d` and :math:`\Gamma_2` are the remaining walls. The Navier
conditions are in effect on both :math:`\Gamma_1`, :math:`\Gamma_2` and are
expressed by the corresponding integrals in the equations above.
The `no-penetration` boundary conditions are applied on :math:`\Gamma_1`,
:math:`\Gamma_2`, except the vertices of the block edges, where the `edge
direction` boundary conditions are applied.
The penalty term formulation is given by the following equations.
Find :math:`\ul{u}`, :math:`p` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \nu\ \nabla \ul{v} : \nabla \ul{u}
- \int_{\Omega} p\ \nabla \cdot \ul{v}
+ \int_{\Gamma_1} \beta \ul{v} \cdot (\ul{u} - \ul{u}_d)
+ \int_{\Gamma_2} \beta \ul{v} \cdot \ul{u}
+ \int_{\Gamma_1 \cup \Gamma_2} \epsilon (\ul{n} \cdot \ul{v})
(\ul{n} \cdot \ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
\int_{\Omega} \mu \nabla q \cdot \nabla p
+ \int_{\Omega} q\ \nabla \cdot \ul{u}
= 0
\;, \quad \forall q \;,
where :math:`\epsilon` is the penalty coefficient (sufficiently large). The
`no-penetration` boundary conditions are applied on :math:`\Gamma_1`,
:math:`\Gamma_2`.
Optionally, Dirichlet boundary conditions can be applied on
the inlet in the both cases, see below.
For large meshes use the ``'ls_i'`` linear solver - PETSc + petsc4py are needed
in that case.
Several parameters can be set using the ``--define`` option of ``sfepy-run``,
see :func:`define()` and the examples below.
Examples
--------
Specify the inlet velocity and a finer mesh::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d shape="(11,31,31),u_inlet=0.5"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Use the penalty term formulation and einsum-based terms with the default
(numpy) backend::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Change backend to opt_einsum (needs to be installed) and use the quadratic velocity approximation order::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "u_order=2,mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum,backend=opt_einsum,optimize=auto"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
Note the pressure field distribution improvement w.r.t. the previous examples. IfPETSc + petsc4py are installed, try using the iterative solver to speed up the solution::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/navier_stokes/stokes_slip_bc -d "u_order=2,ls=ls_i,mode=penalty,term_mode=einsum,backend=opt_einsum,optimize=auto"
sfepy-view -f p:p0 u:o.4:p1 u:g:f0.2:p1 -- user_block.vtk
"""
import os
from functools import partial
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import assert_, output
from sfepy.discrete.fem.meshio import UserMeshIO
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
from sfepy.homogenization.utils import define_box_regions
def define(dims=(3, 1, 0.5), shape=(11, 15, 15), u_order=1, refine=0,
ls='ls_d', u_inlet=None, mode='lcbc', term_mode='original',
backend='numpy', optimize='optimal', verbosity=0, output_dir='.',
save_lcbc_vecs=False):
"""
Parameters
----------
dims : tuple
The block domain dimensions.
shape : tuple
The mesh resolution: increase to improve accuracy.
u_order : int
The velocity field approximation order.
refine : int
The refinement level.
ls : 'ls_d' or 'ls_i'
The pre-configured linear solver name.
u_inlet : float, optional
The x-component of the inlet velocity.
mode : 'lcbc' or 'penalty'
The alternative formulations.
term_mode : 'original' or 'einsum'
The switch to use either the original or new experimental einsum-based
terms.
backend : str
The einsum mode backend.
optimize : str
The einsum mode optimization (backend dependent).
verbosity : 0, 1, 2, 3
The verbosity level of einsum-based terms.
output_dir : str
The output directory.
save_lcbc_vecs : bool
If True, save the no_penetration and edge_direction LCBC vectors.
"""
output('dims: {}, shape: {}, u_order: {}, refine: {}, u_inlet: {}'
.format(dims, shape, u_order, refine, u_inlet))
output('linear solver: {}'.format(ls))
output('mode: {}, term_mode: {}'.format(mode, term_mode))
if term_mode == 'einsum':
output('backend: {}, optimize: {}, verbosity: {}'
.format(backend, optimize, verbosity))
assert_(mode in {'lcbc', 'penalty'})
assert_(term_mode in {'original', 'einsum'})
if u_order > 1:
assert_(mode == 'penalty', msg='set mode=penalty to use u_order > 1!')
dims = nm.array(dims, dtype=nm.float64)
shape = nm.array(shape, dtype=nm.int32)
def mesh_hook(mesh, mode):
"""
Generate the block mesh.
"""
if mode == 'read':
mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, [0, 0, 0], name='user_block',
verbose=False)
return mesh
elif mode == 'write':
pass
filename_mesh = UserMeshIO(mesh_hook)
regions = define_box_regions(3, 0.5 * dims)
regions.update({
'Omega' : 'all',
'Edges_v' : ("""(r.Near *v r.Bottom) +v
(r.Bottom *v r.Far) +v
(r.Far *v r.Top) +v
(r.Top *v r.Near)""", 'edge'),
'Gamma1_f' : ('copy r.Top', 'face'),
'Gamma2_f' : ('r.Near +v r.Bottom +v r.Far', 'face'),
'Gamma_f' : ('r.Gamma1_f +v r.Gamma2_f', 'face'),
'Gamma_v' : ('r.Gamma_f -v r.Edges_v', 'face'),
'Inlet_f' : ('r.Left -v r.Gamma_f', 'face'),
})
fields = {
'velocity' : ('real', 3, 'Omega', u_order),
'pressure' : ('real', 1, 'Omega', 1),
}
def get_u_d(ts, coors, region=None, **kwargs):
"""
Given stator velocity.
"""
out = nm.zeros_like(coors)
out[:] = [1.0, 1.0, 0.0]
return out
functions = {
'get_u_d' : (get_u_d,),
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'velocity', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'velocity', 'u'),
'u_d' : ('parameter field', 'velocity',
{'setter' : 'get_u_d'}),
'p' : ('unknown field', 'pressure', 1),
'q' : ('test field', 'pressure', 'p'),
}
materials = {
'm' : ({
'nu' : 1e-3,
'beta' : 1e-2,
'mu' : 1e-10,
},),
}
ebcs = {
}
if u_inlet is not None:
ebcs['inlet'] = ('Inlet_f', {'u.0' : u_inlet, 'u.[1, 2]' : 0.0})
indir = partial(os.path.join, output_dir)
if mode == 'lcbc':
lcbcs = {
'walls' : ('Gamma_v', {'u.all' : None}, None, 'no_penetration',
indir('normals_Gamma.vtk') if save_lcbc_vecs else None),
'edges' : ('Edges_v', [(-0.5, 1.5)], {'u.all' : None}, None,
'edge_direction',
indir('edges_Edges.vtk') if save_lcbc_vecs else None),
}
if term_mode == 'original':
equations = {
'balance' :
"""dw_div_grad.5.Omega(m.nu, v, u)
- dw_stokes.5.Omega(v, p)
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma2_f(m.beta, v, u)
=
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u_d)""",
'incompressibility' :
"""dw_laplace.5.Omega(m.mu, q, p)
+ dw_stokes.5.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
else:
equations = {
'balance' :
"""de_div_grad.5.Omega(m.nu, v, u)
- de_stokes.5.Omega(v, p)
+ de_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ de_dot.5.Gamma2_f(m.beta, v, u)
=
+ de_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u_d)""",
'incompressibility' :
"""de_laplace.5.Omega(m.mu, q, p)
+ de_stokes.5.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
else:
materials['m'][0]['np_eps'] = 1e3
if term_mode == 'original':
equations = {
'balance' :
"""dw_div_grad.5.Omega(m.nu, v, u)
- dw_stokes.5.Omega(v, p)
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma2_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ dw_non_penetration_p.5.Gamma1_f(m.np_eps, v, u)
+ dw_non_penetration_p.5.Gamma2_f(m.np_eps, v, u)
=
+ dw_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u_d)""",
'incompressibility' :
"""dw_laplace.5.Omega(m.mu, q, p)
+ dw_stokes.5.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
else:
equations = {
'balance' :
"""de_div_grad.5.Omega(m.nu, v, u)
- de_stokes.5.Omega(v, p)
+ de_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ de_dot.5.Gamma2_f(m.beta, v, u)
+ de_non_penetration_p.5.Gamma1_f(m.np_eps, v, u)
+ de_non_penetration_p.5.Gamma2_f(m.np_eps, v, u)
=
+ de_dot.5.Gamma1_f(m.beta, v, u_d)""",
'incompressibility' :
"""de_laplace.5.Omega(m.mu, q, p)
+ de_stokes.5.Omega(u, q) = 0""",
}
solvers = {
'ls_d' : ('ls.auto_direct', {}),
'ls_i' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : 'bcgsl', # ksp_type
'precond' : 'bjacobi', # pc_type
'sub_precond' : 'ilu', # sub_pc_type
'eps_a' : 0.0, # abstol
'eps_r' : 1e-12, # rtol
'eps_d' : 1e10, # Divergence tolerance.
'i_max' : 200, # maxits
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
}),
}
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : ls,
'eterm': {
'verbosity' : verbosity,
'backend_args' : {
'backend' : backend,
'optimize' : optimize,
'layout' : None,
},
},
'refinement_level' : refine,
'output_dir' : output_dir,
}
return locals()