sfepy.solvers.semismooth_newton module¶
- class sfepy.solvers.semismooth_newton.SemismoothNewton(conf, **kwargs)[source]¶
The semi-smooth Newton method.
This method is suitable for solving problems of the following structure:
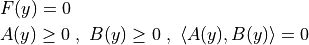
The function
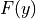 represents the smooth part of the problem.
represents the smooth part of the problem.Regular step:
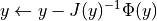
Steepest descent step:
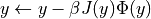
Although
fun_smooth_grad()computes the gradient of the smooth part only, it should return the global matrix, where the non-smooth part is uninitialized, but pre-allocated.Kind: ‘nls.semismooth_newton’
For common configuration parameters, see
Solver.Specific configuration parameters:
- Parameters:
- semismoothbool (default: True)
If True, use the semi-smooth algorithm. Otherwise a non-smooth equation is assumed (use a brute force).
- i_maxint (default: 1)
The maximum number of iterations.
- eps_afloat (default: 1e-10)
The absolute tolerance for the residual, i.e.
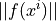 .
.- eps_rfloat (default: 1.0)
The relative tolerance for the residual, i.e.
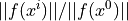 .
.- machepsfloat (default: np.float64(2.220446049250313e-16))
The float considered to be machine “zero”.
- lin_redfloat (default: 1.0)
The linear system solution error should be smaller than (eps_a * lin_red), otherwise a warning is printed.
- ls_onfloat (default: 0.99999)
Start the backtracking line-search by reducing the step, if
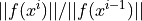 is larger than ls_on.
is larger than ls_on.- ls_reddict (default: {‘regular’: 0.1, ‘steepest_descent’: 0.01})
The step reduction factor in case of correct residual assembling for regular and steepest descent modes.
- ls_red_warp0.0 < float < 1.0 (default: 0.001)
The step reduction factor in case of failed residual assembling (e.g. the “warp violation” error caused by a negative volume element resulting from too large deformations).
- ls_min0.0 < float < 1.0 (default: 1e-05)
The minimum step reduction factor.
- compute_jacobian(vec_x, fun_smooth_grad, fun_a_grad, fun_b_grad, vec_smooth_r, vec_a_r, vec_b_r)[source]¶
- name = 'nls.semismooth_newton'¶