sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators module¶
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, centre, mat_id=0, name='block', coors=None, verbose=True)[source]¶
Generate a 2D or 3D block mesh. The dimension is determined by the lenght of the shape argument.
- Parameters:
- dimsarray of 2 or 3 floats
Dimensions of the block.
- shapearray of 2 or 3 ints
Shape (counts of nodes in x, y, z) of the block mesh.
- centrearray of 2 or 3 floats
Centre of the block.
- mat_idint, optional
The material id of all elements.
- namestring
Mesh name.
- verbosebool
If True, show progress of the mesh generation.
- Returns:
- meshMesh instance
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_cylinder_mesh(dims, shape, centre, axis='x', force_hollow=False, is_open=False, open_angle=0.0, non_uniform=False, make_2d=False, name='cylinder', verbose=True)[source]¶
Generate a cylindrical mesh along an axis. Its cross-section can be ellipsoidal.
- Parameters:
- dimsarray of 5 floats
Dimensions of the cylinder: inner surface semi-axes a1, b1, outer surface semi-axes a2, b2, length. The length can be zero, resulting in a planar annular topology.
- shapearray of 3 ints
Shape (counts of nodes in radial, circumferential and longitudinal directions) of the cylinder mesh.
- centrearray of 3 floats
Centre of the cylinder.
- axis: one of ‘x’, ‘y’, ‘z’
The axis of the cylinder.
- force_hollowboolean
Force hollow mesh even if inner radii a1 = b1 = 0.
- is_openboolean
Generate an open cylinder segment.
- open_anglefloat
Opening angle in radians.
- non_uniformboolean
If True, space the mesh nodes in radial direction so that the element volumes are (approximately) the same, making thus the elements towards the outer surface thinner.
- make_2dboolean
If True, generate an annular mesh in the x-y plane. Sets length to 0.
- namestring
Mesh name.
- verbosebool
If True, show progress of the mesh generation.
- Returns:
- meshMesh instance
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_extended_block_mesh(b_dims, b_shape, e_dims, e_shape, centre, grading_fun=None, name=None)[source]¶
Generate a 3D mesh with a central block and (coarse) extending side meshes.
The resulting mesh is again a block. Each of the components has a different material id.
- Parameters:
- b_dimsarray of 3 floats
The dimensions of the central block.
- b_shapearray of 3 ints
The shape (counts of nodes in x, y, z) of the central block mesh.
- e_dimsarray of 3 floats
The dimensions of the complete block (central block + extensions).
- e_shapeint
The count of nodes of extending blocks in the direction from the central block.
- centrearray of 3 floats
The centre of the mesh.
- grading_funcallable, optional
A function of
![x \in [0, 1]](../../../_images/math/dc674c35000b0090c61f0a465110039e98461cef.png) that can be used to shift nodes in
the extension axis directions to allow smooth grading of element sizes
from the centre. The default function is
that can be used to shift nodes in
the extension axis directions to allow smooth grading of element sizes
from the centre. The default function is 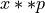 with
with 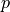 determined so that the element sizes next to the central block have the
size of the shortest edge of the central block.
determined so that the element sizes next to the central block have the
size of the shortest edge of the central block.- namestring, optional
The mesh name.
- Returns:
- meshMesh instance
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_mesh_from_geom(geo, a=None, verbose=False, refine=False)[source]¶
Runs mesh generator - tetgen for 3D or triangle for 2D meshes.
- Parameters:
- geogeometry
geometry description
- aint, optional
a maximum area/volume constraint
- verbosebool, optional
detailed information
- refinebool, optional
refines mesh
- Returns:
- meshMesh instance
triangular or tetrahedral mesh
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_mesh_from_voxels(voxels, dims, etype='q')[source]¶
Generate FE mesh from voxels (volumetric data).
- Parameters:
- voxelsarray
Voxel matrix, 1=material.
- dimsarray
Size of one voxel.
- etypeinteger, optional
‘q’ - quadrilateral or hexahedral elements ‘t’ - triangular or tetrahedral elements
- Returns
- ——-
- meshMesh instance
Finite element mesh.
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_misc_mesh(mesh_dir, force_create, kind, args, suffix='.mesh', verbose=False)[source]¶
Create sphere or cube mesh according to kind in the given directory if it does not exist and return path to it.
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.gen_tiled_mesh(mesh, grid=None, scale=1.0, eps=1e-06, ret_ndmap=False)[source]¶
Generate a new mesh by repeating a given periodic element along each axis.
- Parameters:
- meshMesh instance
The input periodic FE mesh.
- gridarray
Number of repetition along each axis.
- scalefloat, optional
Scaling factor.
- epsfloat, optional
Tolerance for boundary detection.
- ret_ndmapbool, optional
If True, return global node map.
- Returns:
- mesh_outMesh instance
FE mesh.
- ndmaparray
Maps: actual node id –> node id in the reference cell.
- sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators.get_tensor_product_conn(shape)[source]¶
Generate vertex connectivity for cells of a tensor-product mesh of the given shape.
- Parameters:
- shapearray of 2 or 3 ints
Shape (counts of nodes in x, y, z) of the mesh.
- Returns:
- connarray
The vertex connectivity array.
- descstr
The cell kind.