sfepy.discrete.fem.fields_base module¶
Notes¶
Important attributes of continuous (order > 0) Field and
SurfaceField instances:
vertex_remap : econn[:, :n_vertex] = vertex_remap[conn]
vertex_remap_i : conn = vertex_remap_i[econn[:, :n_vertex]]
where conn is the mesh vertex connectivity, econn is the region-local field connectivity.
- class sfepy.discrete.fem.fields_base.FEField(name, dtype, shape, region, approx_order=1)[source]¶
Base class for finite element fields.
Notes
interps and hence node_descs are per region (must have single geometry!)
Field shape information:
shape- the shape of the basis functions in a pointn_components- the number of DOFs per FE nodeval_shape- the shape of field value (the product of DOFs and basis functions) in a point
- average_qp_to_vertices(data_qp, integral)[source]¶
Average data given in quadrature points in region elements into region vertices.
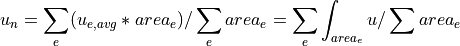
- create_mapping(region, integral, integration, return_mapping=True)[source]¶
Create a new reference mapping.
Compute jacobians, element volumes and basis function derivatives for Volume-type geometries (volume mappings), and jacobians, normals and basis function derivatives for Surface-type geometries (surface mappings).
Notes
surface mappings are defined on the surface region
surface mappings require field order to be > 0
- create_mesh(extra_nodes=True)[source]¶
Create a mesh from the field region, optionally including the field extra nodes.
- create_output(dofs, var_name, dof_names=None, key=None, extend=True, fill_value=None, linearization=None)[source]¶
Convert the DOFs corresponding to the field to a dictionary of output data usable by Mesh.write().
- Parameters:
- dofsarray, shape (n_nod, n_component)
The array of DOFs reshaped so that each column corresponds to one component.
- var_namestr
The variable name corresponding to dofs.
- dof_namestuple of str
The names of DOF components.
- keystr, optional
The key to be used in the output dictionary instead of the variable name.
- extendbool
Extend the DOF values to cover the whole domain.
- fill_valuefloat or complex
The value used to fill the missing DOF values if extend is True.
- linearizationStruct or None
The linearization configuration for higher order approximations.
- Returns:
- outdict
The output dictionary.
- extend_dofs(dofs, fill_value=None)[source]¶
Extend DOFs to the whole domain using the fill_value, or the smallest value in dofs if fill_value is None.
- get_coor(nods=None)[source]¶
Get coordinates of the field nodes.
- Parameters:
- nodsarray, optional
The indices of the required nodes. If not given, the coordinates of all the nodes are returned.
- get_data_shape(integral, integration='cell', region_name=None)[source]¶
Get element data dimensions.
- Parameters:
- integralIntegral instance
The integral describing used numerical quadrature.
- integration‘cell’, ‘facet’, ‘facet_extra’, ‘point’ or ‘custom’
The term integration mode.
- region_namestr
The name of the region of the integral.
- Returns:
- data_shape4 ints
The (n_el, n_qp, dim, n_en) for volume shape kind, (n_fa, n_qp, dim, n_fn) for surface shape kind and (n_nod, 0, 0, 1) for point shape kind.
Notes
Integration modes: - ‘cell’: integration over cells/elements - ‘facet’: integration over cell facets (faces, edges) - ‘facet_extra’: same as ‘facet’ but also the normal derivatives
are evaluated
‘point’: point integration
‘custom’: user defined integration
Dimensions: - n_el, n_fa = number of elements/facets - n_qp = number of quadrature points per element/facet - dim = spatial dimension - n_en, n_fn = number of element/facet nodes - n_nod = number of element nodes
- get_dofs_in_region(region, merge=True)[source]¶
Return indices of DOFs that belong to the given region.
- get_econn(conn_type, region, trace_region=None, local=False)[source]¶
Get extended connectivity of the given type in the given region.
- Parameters:
- conn_type: tuple or string
DOF connectivity type, eg. (‘cell’, 3) or ‘cell’. If the topological dimension not specified, it is taken from region.tdim.
- region: sfepy.discrete.common.region.Region
The region for which the connectivity is required.
- trace_region: None or string
If not None, return mirror connectivity according to local.
- local: bool
If True, return local connectivity w.r.t. facet nodes, otherwise return global connectivity w.r.t. all mesh nodes.
- Returns:
- econn: numpy.ndarray
The extended connectivity array.
- get_evaluate_cache(cache=None, share_geometry=False, verbose=False)[source]¶
Get the evaluate cache for
Variable.evaluate_at().- Parameters:
- cacheStruct instance, optional
Optionally, use the provided instance to store the cache data.
- share_geometrybool
Set to True to indicate that all the evaluations will work on the same region. Certain data are then computed only for the first probe and cached.
- verbosebool
If False, reduce verbosity.
- Returns:
- cacheStruct instance
The evaluate cache.
- get_qp(key, integral)[source]¶
Get quadrature points and weights corresponding to the given key and integral. The key is ‘v’, ‘s#’ or ‘b#’, where # is the number of face vertices. For ‘b#’, the quadrature must already be created by calling
FEField.create_bqp(), usually throughFEField.create_mapping().
- get_true_order()[source]¶
Get the true approximation order depending on the reference element geometry.
For example, for P1 (linear) approximation the true order is 1, while for Q1 (bilinear) approximation in 2D the true order is 2.
- interp_to_qp(dofs)[source]¶
Interpolate DOFs into quadrature points.
The quadrature order is given by the field approximation order.
- Parameters:
- dofsarray
The array of DOF values of shape (n_nod, n_component).
- Returns:
- data_qparray
The values interpolated into the quadrature points.
- integralIntegral
The corresponding integral defining the quadrature points.
- linearize(dofs, min_level=0, max_level=1, eps=0.0001)[source]¶
Linearize the solution for post-processing.
- Parameters:
- dofsarray, shape (n_nod, n_component)
The array of DOFs reshaped so that each column corresponds to one component.
- min_levelint
The minimum required level of mesh refinement.
- max_levelint
The maximum level of mesh refinement.
- epsfloat
The relative tolerance parameter of mesh adaptivity.
- Returns:
- meshMesh instance
The adapted, nonconforming, mesh.
- vdofsarray
The DOFs defined in vertices of mesh.
- levelsarray of ints
The refinement level used for each element group.
- restore_dofs(store=False)[source]¶
Undoes the effect of
FEField.substitute_dofs().
- restore_substituted(vec)[source]¶
Restore values of the unused DOFs using the transpose of the applied basis transformation.
- set_basis_transform(transform)[source]¶
Set local element basis transformation.
The basis transformation is applied in
FEField.eval_basis()andFEField.create_mapping().- Parameters:
- transformarray, shape (n_cell, n_ep, n_ep)
The array with (n_ep, n_ep) transformation matrices for each cell in the field’s region, where n_ep is the number of element DOFs.
- class sfepy.discrete.fem.fields_base.H1Mixin(**kwargs)[source]¶
Methods of fields specific to H1 space.
- sfepy.discrete.fem.fields_base.create_expression_output(expression, name, primary_field_name, fields, materials, variables, functions=None, mode='eval', term_mode=None, extra_args=None, verbose=True, kwargs=None, min_level=0, max_level=1, eps=0.0001)[source]¶
Create output mesh and data for the expression using the adaptive linearizer.
- Parameters:
- expressionstr
The expression to evaluate.
- namestr
The name of the data.
- primary_field_namestr
The name of field that defines the element groups and polynomial spaces.
- fieldsdict
The dictionary of fields used in variables.
- materialsMaterials instance
The materials used in the expression.
- variablesVariables instance
The variables used in the expression.
- functionsFunctions instance, optional
The user functions for materials etc.
- modeone of ‘eval’, ‘el_avg’, ‘qp’
The evaluation mode - ‘qp’ requests the values in quadrature points, ‘el_avg’ element averages and ‘eval’ means integration over each term region.
- term_modestr
The term call mode - some terms support different call modes and depending on the call mode different values are returned.
- extra_argsdict, optional
Extra arguments to be passed to terms in the expression.
- verbosebool
If False, reduce verbosity.
- kwargsdict, optional
The variables (dictionary of (variable name) : (Variable instance)) to be used in the expression.
- min_levelint
The minimum required level of mesh refinement.
- max_levelint
The maximum level of mesh refinement.
- epsfloat
The relative tolerance parameter of mesh adaptivity.
- Returns:
- outdict
The output dictionary.
- sfepy.discrete.fem.fields_base.eval_nodal_coors(coors, mesh_coors, region, poly_space, geom_poly_space, econn, only_extra=True)[source]¶
Compute coordinates of nodes corresponding to poly_space, given mesh coordinates and geom_poly_space.