linear_elasticity/seismic_load.py¶
Description
The linear elastodynamics of an elastic body loaded by a given base motion.
Find 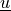 such that:
such that:
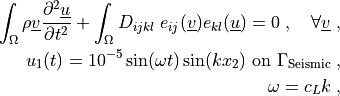
where 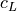 is the longitudinal wave propagation speed,
is the longitudinal wave propagation speed, 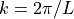 ,`
,` 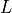 is the length of the domain and
is the length of the domain and
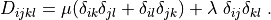
See linear_elasticity/elastodynamic.py example for notes on elastodynamics solvers.
Usage Examples¶
Run with the default settings (the Newmark method, 2D problem, results stored
in output/seismic/):
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/seismic_load.py -o tsn
View the resulting displacements on the deforming mesh (10x magnified):
sfepy-view output/seismic/tsn.h5 -2 -f u:wu:f10:p0 1:vw:p0
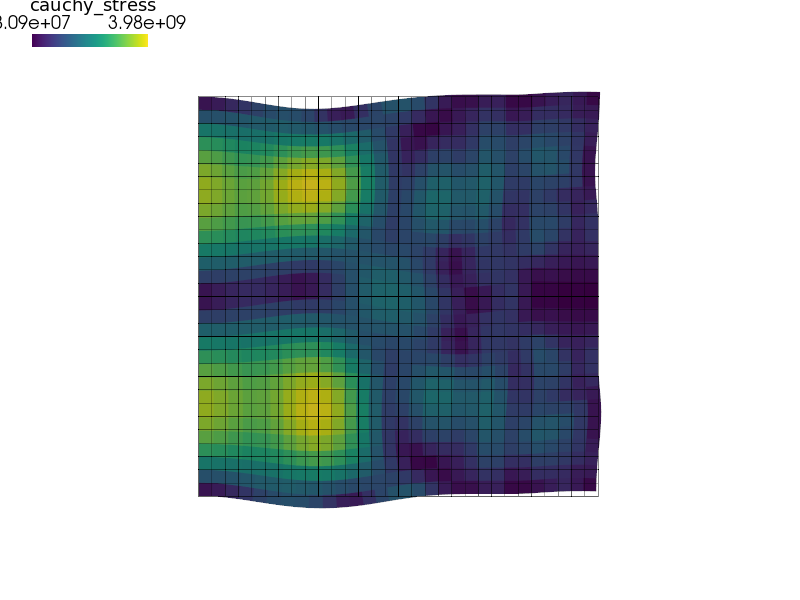
Use the central difference explicit method with the reciprocal mass matrix algorithm [1] and view the resulting stress waves:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/seismic_load.py -d "dims=(5e-3, 5e-3), shape=(51, 51), tss_name=tscd, ls_name=lsrmm, mass_beta=0.5, mass_lumping=row_sum, fast_rmm=True, save_times=all" -o tscd
sfepy-view output/seismic/tscd.h5 -2 -f cauchy_stress:wu:f10:p0 1:vw:p0
r"""
The linear elastodynamics of an elastic body loaded by a given base motion.
Find :math:`\ul{u}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} \rho \ul{v} \pddiff{\ul{u}}{t}
+ \int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
= 0
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;, \\
u_1(t) = 10^{-5} \sin(\omega t) \sin(k x_2)
\mbox{ on } \Gamma_\mathrm{Seismic} \;, \\
\omega = c_L k \;,
where :math:`c_L` is the longitudinal wave propagation speed, :math:`k = 2 \pi
/ L`,` :math:`L` is the length of the domain and
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
See :ref:`linear_elasticity-elastodynamic` example for notes on elastodynamics
solvers.
Usage Examples
--------------
Run with the default settings (the Newmark method, 2D problem, results stored
in ``output/seismic/``)::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/seismic_load.py -o tsn
View the resulting displacements on the deforming mesh (10x magnified)::
sfepy-view output/seismic/tsn.h5 -2 -f u:wu:f10:p0 1:vw:p0
Use the central difference explicit method with the reciprocal mass matrix
algorithm [1]_ and view the resulting stress waves::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/seismic_load.py -d "dims=(5e-3, 5e-3), shape=(51, 51), tss_name=tscd, ls_name=lsrmm, mass_beta=0.5, mass_lumping=row_sum, fast_rmm=True, save_times=all" -o tscd
sfepy-view output/seismic/tscd.h5 -2 -f cauchy_stress:wu:f10:p0 1:vw:p0
.. [1] González, J.A., Kolman, R., Cho, S.S., Felippa, C.A., Park, K.C., 2018.
Inverse mass matrix via the method of localized Lagrange multipliers.
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 113, 277–295.
https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5613
"""
import numpy as nm
import sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs as mc
from sfepy.discrete.fem.meshio import UserMeshIO
from sfepy.mesh.mesh_generators import gen_block_mesh
def define(
E=200e9, nu=0.3, rho=7800,
plane='strain',
dims=(5e-3, 5e-3),
shape=(31, 31),
v0=1.0,
ct1=1.5,
dt=None,
edt_safety=0.2,
tss_name='tsn',
tsc_name='tscedl',
adaptive=False,
ls_name='lsd',
mass_beta=0.0,
mass_lumping='none',
fast_rmm=False,
active_only=False,
save_times=20,
output_dir='output/seismic',
):
"""
Parameters
----------
E, nu, rho: material parameters
plane: plane strain or stress hypothesis
dims: physical dimensions of the block (L, d, x)
shape: numbers of mesh vertices along each axis
v0: initial impact velocity
ct1: final time in L / "longitudinal wave speed" units
dt: time step (None means automatic)
edt_safety: safety factor time step multiplier for explicit schemes,
if dt is None
tss_name: time stepping solver name (see "solvers" section)
tsc_name: time step controller name (see "solvers" section)
adaptive: use adaptive time step control
ls_name: linear system solver name (see "solvers" section)
mass_beta: averaged mass matrix parameter 0 <= beta <= 1
mass_lumping: mass matrix lumping ('row_sum', 'hrz' or 'none')
fast_rmm: use zero inertia term with lsrmm
save_times: number of solutions to save
output_dir: output directory
"""
dim = len(dims)
lam, mu = mc.lame_from_youngpoisson(E, nu, plane=plane)
# Longitudinal and shear wave propagation speeds.
cl = nm.sqrt((lam + 2.0 * mu) / rho)
cs = nm.sqrt(mu / rho)
# Element size.
L, d = dims[:2]
H = L / (nm.max(shape) - 1)
# Time-stepping parameters.
if dt is None:
# For implicit schemes, dt based on the Courant number C0 = dt * cl / H
# equal to 1.
dt = H / cl # C0 = 1
if tss_name in ('tsvv', 'tscd'):
# For explicit schemes, use a safety margin.
dt *= edt_safety
t1 = ct1 * L / cl
def mesh_hook(mesh, mode):
"""
Generate the block mesh.
"""
if mode == 'read':
mesh = gen_block_mesh(dims, shape, 0.5 * nm.array(dims),
name='user_block', verbose=False)
return mesh
elif mode == 'write':
pass
def post_process(out, problem, state, extend=False):
"""
Calculate and output strain and stress for given displacements.
"""
from sfepy.base.base import Struct
ev = problem.evaluate
strain = ev('ev_cauchy_strain.i.Omega(u)', mode='el_avg', verbose=False)
stress = ev('ev_cauchy_stress.i.Omega(solid.D, u)', mode='el_avg',
copy_materials=False, verbose=False)
out['cauchy_strain'] = Struct(name='output_data', mode='cell',
data=strain)
out['cauchy_stress'] = Struct(name='output_data', mode='cell',
data=stress)
return out
filename_mesh = UserMeshIO(mesh_hook)
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Seismic' : ('vertices in (x < 1e-12)', 'facet'),
}
# Iron.
materials = {
'solid' : ({
'D': mc.stiffness_from_youngpoisson(dim=dim, young=E, poisson=nu,
plane=plane),
'rho': rho,
'.lumping' : mass_lumping,
'.beta' : mass_beta,
},),
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 'vector', 'Omega', 1),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2,
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
}
def get_ebcs(ts, coors, mode='u'):
y = coors[:, 1]
amplitude = 0.00001
k = 2 * nm.pi / L
omega = cl * k
if mode == 'u':
val = amplitude * nm.sin(ts.time * omega) * nm.sin(k * y)
elif mode == 'du':
val = amplitude * omega * nm.cos(ts.time * omega) * nm.sin(k * y)
elif mode == 'ddu':
val = -amplitude * omega**2 * nm.sin(ts.time * omega) * nm.sin(k * y)
return val
functions = {
'get_u' : (lambda ts, coor, **kwargs: get_ebcs(ts, coor),),
'get_du' : (lambda ts, coor, **kwargs: get_ebcs(ts, coor, mode='du'),),
'get_ddu' : (lambda ts, coor, **kwargs: get_ebcs(ts, coor, mode='ddu'),),
}
ebcs = {
'Seismic' : ('Seismic', {'u.0' : 'get_u', 'du.0' : 'get_du',
'ddu.0' : 'get_ddu'}),
}
ics = {
'ic' : ('Omega', {'u.all' : 0.0, 'du.all' : 0.0}),
}
if (ls_name == 'lsrmm') and fast_rmm:
# Speed up residual calculation, as M is not used with lsrmm.
term = 'dw_zero.i.Omega(v, ddu)'
else:
term = 'de_mass.i.Omega(solid.rho, solid.lumping, solid.beta, v, ddu)'
equations = {
'balance_of_forces' :
term + '+ dw_lin_elastic.i.Omega(solid.D, v, u) = 0',
}
solvers = {
'lsd' : ('ls.auto_direct', {
# Reuse the factorized linear system from the first time step.
'use_presolve' : True,
# Speed up the above by omitting the matrix digest check used
# normally for verification that the current matrix corresponds to
# the factorized matrix stored in the solver instance. Use with
# care!
'use_mtx_digest' : False,
}),
'lsi' : ('ls.petsc', {
'method' : 'cg',
'precond' : 'icc',
'i_max' : 150,
'eps_a' : 1e-32,
'eps_r' : 1e-8,
'verbose' : 2,
}),
'lsrmm' : ('ls.rmm', {
'rmm_term' : """de_mass.i.Omega(solid.rho, solid.lumping,
solid.beta, v, ddu)""",
'debug' : False,
}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton', {
'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-6,
'eps_r' : 1e-6,
'ls_on' : 1e100,
}),
'tsvv' : ('ts.velocity_verlet', {
# Explicit method.
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
'tscd' : ('ts.central_difference', {
# Explicit method. Supports ls.rmm.
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
'tsn' : ('ts.newmark', {
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'beta' : 0.25,
'gamma' : 0.5,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
'tsga' : ('ts.generalized_alpha', {
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'rho_inf' : 0.5,
'alpha_m' : None,
'alpha_f' : None,
'beta' : None,
'gamma' : None,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
'tsb' : ('ts.bathe', {
't0' : 0.0,
't1' : t1,
'dt' : dt,
'n_step' : None,
'is_linear' : True,
'verbose' : 1,
}),
'tscedb' : ('tsc.ed_basic', {
'eps_r' : (1e-4, 1e-1),
'eps_a' : (1e-8, 5e-2),
'fmin' : 0.3,
'fmax' : 2.5,
'fsafety' : 0.85,
}),
'tscedl' : ('tsc.ed_linear', {
'eps_r' : (1e-4, 1e-1),
'eps_a' : (1e-8, 5e-2),
'fmin' : 0.3,
'fmax' : 2.5,
'fsafety' : 0.85,
'red_factor' : 0.9,
'inc_wait' : 10,
'min_inc_factor' : 1.5,
}),
}
options = {
'ts' : tss_name,
'tsc' : tsc_name if adaptive else None,
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : ls_name,
'save_times' : save_times,
'active_only' : active_only,
'auto_transform_equations' : True,
'output_format' : 'h5',
'output_dir' : output_dir,
'post_process_hook' : 'post_process',
}
return locals()