linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py¶
Description
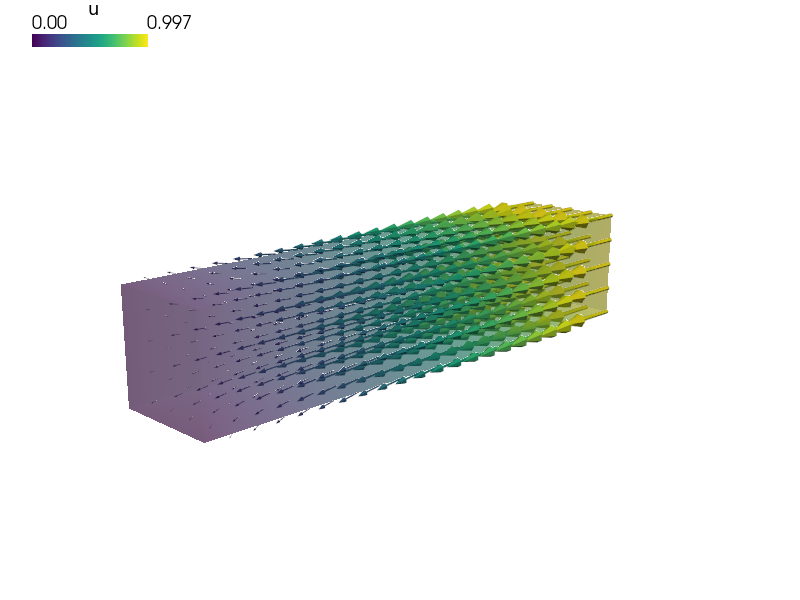
Linear elasticity with pressure traction load on a surface and constrained to one-dimensional motion.
Find 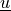 such that:
such that:
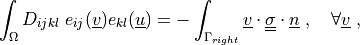
where
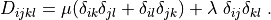
and 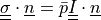 with given traction pressure
with given traction pressure 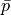 .
.
The function verify_tractions() is called after the solution to verify
that the inner surface tractions correspond to the load applied to the external
surface. Try running the example with different approximation orders and/or uniform refinement levels:
the default options:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=0 -d approx_order=1
refine once:
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=1 -d approx_order=1
use the tri-quadratic approximation (Q2):
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=0 -d approx_order=2
r"""
Linear elasticity with pressure traction load on a surface and constrained to
one-dimensional motion.
Find :math:`\ul{u}` such that:
.. math::
\int_{\Omega} D_{ijkl}\ e_{ij}(\ul{v}) e_{kl}(\ul{u})
= - \int_{\Gamma_{right}} \ul{v} \cdot \ull{\sigma} \cdot \ul{n}
\;, \quad \forall \ul{v} \;,
where
.. math::
D_{ijkl} = \mu (\delta_{ik} \delta_{jl}+\delta_{il} \delta_{jk}) +
\lambda \ \delta_{ij} \delta_{kl}
\;.
and :math:`\ull{\sigma} \cdot \ul{n} = \bar{p} \ull{I} \cdot \ul{n}`
with given traction pressure :math:`\bar{p}`.
The function :func:`verify_tractions()` is called after the solution to verify
that the inner surface tractions correspond to the load applied to the external
surface. Try running the example with different approximation orders and/or uniform refinement levels:
- the default options::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=0 -d approx_order=1
- refine once::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=1 -d approx_order=1
- use the tri-quadratic approximation (Q2)::
sfepy-run sfepy/examples/linear_elasticity/linear_elastic_tractions.py -O refinement_level=0 -d approx_order=2
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
import numpy as nm
from sfepy.base.base import output
from sfepy.mechanics.matcoefs import stiffness_from_lame
def linear_tension(ts, coor, mode=None, **kwargs):
if mode == 'qp':
val = nm.tile(1.0, (coor.shape[0], 1, 1))
return {'val' : val}
def verify_tractions(out, problem, state, extend=False):
"""
Verify that the inner surface tractions correspond to the load applied
to the external surface.
"""
from sfepy.mechanics.tensors import get_full_indices
from sfepy.discrete import Material, Function
load_force = problem.evaluate(
'ev_integrate_mat.2.Right(load.val, u)'
)
output('surface load force:', load_force)
def eval_force(region_name):
strain = problem.evaluate(
'ev_cauchy_strain.i.%s(u)' % region_name, mode='qp',
verbose=False,
)
D = problem.evaluate(
'ev_integrate_mat.i.%s(solid.D, u)' % region_name,
mode='qp',
verbose=False,
)
normal = nm.array([1, 0, 0], dtype=nm.float64)
s2f = get_full_indices(len(normal))
stress = nm.einsum('cqij,cqjk->cqik', D, strain)
# Full (matrix) form of stress.
mstress = stress[..., s2f, 0]
# Force in normal direction.
force = nm.einsum('cqij,i,j->cq', mstress, normal, normal)
def get_force(ts, coors, mode=None, **kwargs):
if mode == 'qp':
return {'force' : force.reshape(coors.shape[0], 1, 1)}
aux = Material('aux', function=Function('get_force', get_force))
middle_force = - problem.evaluate(
'ev_integrate_mat.i.%s(aux.force, u)' % region_name,
aux=aux,
verbose=False,
)
output('%s section axial force:' % region_name, middle_force)
eval_force('Left')
eval_force('Middle')
eval_force('Right')
return out
def define(approx_order=1):
"""Define the problem to solve."""
from sfepy import data_dir
filename_mesh = data_dir + '/meshes/3d/block.mesh'
options = {
'nls' : 'newton',
'ls' : 'ls',
'post_process_hook' : 'verify_tractions',
}
functions = {
'linear_tension' : (linear_tension,),
}
fields = {
'displacement': ('real', 3, 'Omega', approx_order),
}
materials = {
'solid' : ({'D': stiffness_from_lame(3, lam=5.769, mu=3.846)},),
'load' : (None, 'linear_tension')
}
variables = {
'u' : ('unknown field', 'displacement', 0),
'v' : ('test field', 'displacement', 'u'),
}
regions = {
'Omega' : 'all',
'Left' : ('vertices in (x < -4.99)', 'facet'),
# Use a parent region to select only facets belonging to cells in the
# parent region. Otherwise, each facet is in the region two times, with
# opposite normals.
'Middle' : ('vertices in (x > -1e-10) & (x < 1e-10)', 'facet', 'Rhalf'),
'Rhalf' : 'vertices in x > -1e-10',
'Right' : ('vertices in (x > 4.99)', 'facet'),
}
ebcs = {
'fixb' : ('Left', {'u.all' : 0.0}),
'fixt' : ('Right', {'u.[1,2]' : 0.0}),
}
integrals = {
'i' : 2 * approx_order,
}
##
# Balance of forces.
equations = {
'elasticity' :
"""dw_lin_elastic.i.Omega( solid.D, v, u )
= - dw_surface_ltr.i.Right( load.val, v )""",
}
##
# Solvers etc.
solvers = {
'ls' : ('ls.auto_direct', {}),
'newton' : ('nls.newton',
{ 'i_max' : 1,
'eps_a' : 1e-10,
'eps_r' : 1.0,
'macheps' : 1e-16,
# Linear system error < (eps_a * lin_red).
'lin_red' : 1e-2,
'ls_red' : 0.1,
'ls_red_warp' : 0.001,
'ls_on' : 1.1,
'ls_min' : 1e-5,
'check' : 0,
'delta' : 1e-6,
})
}
return locals()